1. The method of scientific inquiry that describes natural structures and processes as accurately as possible through careful observation and the analysis of data is known as
a) hypothesis-based science.
b) experimental science.
c) discovery science.
d) qualitative science.
2. Collecting data based on observation is an example of---------; analyzing this data to reach a conclusion is an example of ------- reasoning. a) hypothesis-based science; inductive
b) discovery science; inductive
c) the process of science; deductive
d) descriptive science; deductive
3. When applying the process of science, which of these is tested?
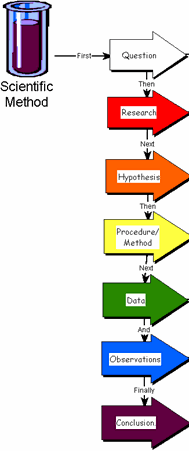 a) a question
a) a question
b) an observation
c) a hypothesis
d) a prediction
4. A controlled experiment is one in which
a) the experiment proceeds at a slow pace to guarantee that the scientist can carefully observe all reactions and process all experimental data.
b) there are at least two groups, one of which does not receive the experimental treatment.
c) there are at least two groups, one differing from the other by two or more variables.
d) there is one group for which the scientist controls all variables.
5. Why is it important that an experiment include a control group?
a) The control group is the group that the researcher is in control of, the group in which the researcher predetermines the results.
b) The control group provides a reserve of experimental subjects.
c) A control group assures that an experiment will be repeatable.
d) Without a control group, there is no basis for knowing if a particular result is due to the variable being tested.
6. The application of scientific knowledge for some specific purpose is known as a) technology.
b) deductive science.
c) inductive science.
d) pure science.
7. Which of the following are qualities of any good scientific hypothesis?
I. It is testable.
II. It is falsifiable.
III. It produces quantitative data.
IV. It produces results that can be replicated.
a) I only
b) II only
c) III only
d) I and II
8. When a hypothesis cannot be written in an "If…then" format, what does this mean? a) It does not represent deductive reasoning.
b) It cannot be a scientific hypothesis.
c) The subject cannot be explored scientifically.
d) The hypothesizer does not have sufficient information.
9. In presenting data that result from an experiment, a group of students show that most of their measurements fall on a straight diagonal line on their graph. However, two of their data points are "outliers" and fall far to one side of the expected relationship. What should they do?
a) Do not show these points but write a footnote that the graph represents the correct data.
b) Average several trials and therefore rule out the improbable results.
c) Show all results obtained and then try to explore the reason(s) for these outliers.
d) Change the details of the experiment until they can obtain the expected results.
10. Which of the following is the best description of a control for an experiment?
a) The control group is kept in an unchanging environment.
b) The control is left alone by the experimenters.
c) The control group is matched with the experimental group except for the one experimental variable.
d) The control group is exposed to only one variable rather than several.
Learn more:
1. c) discovery science.
2. b) discovery science; inductive
3. d) a prediction
4. b) there are at least two groups, one of which does not receive the experimental treatment.
5. d) Without a control group, there is no basis for knowing if a particular result is due to the variable being tested.
6. a) technology.
7. d) I and II
8. a) It does not represent deductive reasoning.
9. c) Show all results obtained and then try to explore the reason(s) for these outliers.
10. c) The control group is matched with the experimental group except for the one experimental variable.
a) hypothesis-based science.
b) experimental science.
c) discovery science.
d) qualitative science.
2. Collecting data based on observation is an example of---------; analyzing this data to reach a conclusion is an example of ------- reasoning. a) hypothesis-based science; inductive
b) discovery science; inductive
c) the process of science; deductive
d) descriptive science; deductive
3. When applying the process of science, which of these is tested?
 a) a question
a) a question b) an observation
c) a hypothesis
d) a prediction
4. A controlled experiment is one in which
a) the experiment proceeds at a slow pace to guarantee that the scientist can carefully observe all reactions and process all experimental data.
b) there are at least two groups, one of which does not receive the experimental treatment.
c) there are at least two groups, one differing from the other by two or more variables.
d) there is one group for which the scientist controls all variables.
5. Why is it important that an experiment include a control group?
a) The control group is the group that the researcher is in control of, the group in which the researcher predetermines the results.
b) The control group provides a reserve of experimental subjects.
c) A control group assures that an experiment will be repeatable.
d) Without a control group, there is no basis for knowing if a particular result is due to the variable being tested.
6. The application of scientific knowledge for some specific purpose is known as a) technology.
b) deductive science.
c) inductive science.
d) pure science.
7. Which of the following are qualities of any good scientific hypothesis?
I. It is testable.
II. It is falsifiable.
III. It produces quantitative data.
IV. It produces results that can be replicated.
a) I only
b) II only
c) III only
d) I and II
8. When a hypothesis cannot be written in an "If…then" format, what does this mean? a) It does not represent deductive reasoning.
b) It cannot be a scientific hypothesis.
c) The subject cannot be explored scientifically.
d) The hypothesizer does not have sufficient information.
9. In presenting data that result from an experiment, a group of students show that most of their measurements fall on a straight diagonal line on their graph. However, two of their data points are "outliers" and fall far to one side of the expected relationship. What should they do?
a) Do not show these points but write a footnote that the graph represents the correct data.
b) Average several trials and therefore rule out the improbable results.
c) Show all results obtained and then try to explore the reason(s) for these outliers.
d) Change the details of the experiment until they can obtain the expected results.
10. Which of the following is the best description of a control for an experiment?
a) The control group is kept in an unchanging environment.
b) The control is left alone by the experimenters.
c) The control group is matched with the experimental group except for the one experimental variable.
d) The control group is exposed to only one variable rather than several.
Learn more:
- Multiple Choice Questions on Scientific Method
- Multiple Choice Questions on Scientific Method : Experimentation in Science
1. c) discovery science.
2. b) discovery science; inductive
3. d) a prediction
4. b) there are at least two groups, one of which does not receive the experimental treatment.
5. d) Without a control group, there is no basis for knowing if a particular result is due to the variable being tested.
6. a) technology.
7. d) I and II
8. a) It does not represent deductive reasoning.
9. c) Show all results obtained and then try to explore the reason(s) for these outliers.
10. c) The control group is matched with the experimental group except for the one experimental variable.