11. Biological organisation starts with
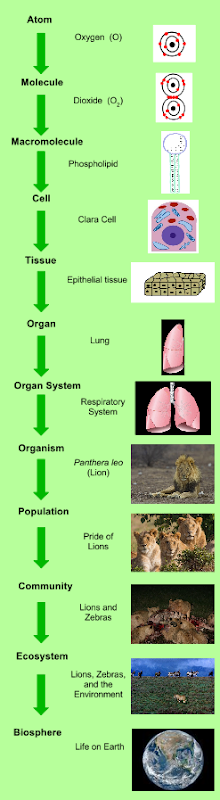
a) Atomic level
b) Submicroscopic molecular level
c) Cellular level
d) Organism level
12. Which one of the following is an amine hormone?
a) Progesterone
b) Thyroxine
c) Oxypurin
d) Insulin
13. Select one of the following of important features distinguishing Gnetum from Cycas and Pinus and showing affinities with angiosperms
a) Embryo development and apical meristem
b) Absence of resin duct and leaf venation
c) Presence of vessel elements and absence of archegonia
d) Perianth and two integuments
14. Thermococcus, Methanococcus and Methanobacterium exemplify

b) Submicroscopic molecular level
c) Cellular level
d) Organism level
12. Which one of the following is an amine hormone?
a) Progesterone
b) Thyroxine
c) Oxypurin
d) Insulin
13. Select one of the following of important features distinguishing Gnetum from Cycas and Pinus and showing affinities with angiosperms
a) Embryo development and apical meristem
b) Absence of resin duct and leaf venation
c) Presence of vessel elements and absence of archegonia
d) Perianth and two integuments
14. Thermococcus, Methanococcus and Methanobacterium exemplify
a) Bacteria that contain a cytoskeleton and ribosomes
b) Archaebacteria that contain protein homologous to eukaryotic core histones
c) Archaebacteria that lack any histones resembling those found in eukaryotes but whose DNA is negatively supercoiled
d) Bacteria whose DNA is relaxed or positively supercoiled but which have a cytoskeleton as well as mitochondria
15. Which one of the following is heterosporous?
b) Archaebacteria that contain protein homologous to eukaryotic core histones
c) Archaebacteria that lack any histones resembling those found in eukaryotes but whose DNA is negatively supercoiled
d) Bacteria whose DNA is relaxed or positively supercoiled but which have a cytoskeleton as well as mitochondria
15. Which one of the following is heterosporous?
a) Equisetum
b) Dryopteris
c) Salvinia
d) Adiantum
16. In which one of the following male and female gametophytes do not have free-living independent existence?
a) Cedrus
b) Pteris
c) Funaria
d) Polytrichum
17. T.O. Diener discovered a
a) free infectious DNA
b) infectious protein
c) bacteriophage
d) free infectious RNA
18. Montreal Protocol aims at?
a) biodiversity conservation
b) control of water pollution
c) control of carbon dioxide emission
d) reduction of ozone-depleting substances
19. Male and female gametophytes are independent and free-living in?
a) mustard
b) castor
c) Pinus
d) sphagnum
20. Which one of the following is not used in organic farming?
a) Glomus
b) Oscillatoria
c) Snail
d) Earthworm
b) Dryopteris
c) Salvinia
d) Adiantum
16. In which one of the following male and female gametophytes do not have free-living independent existence?
a) Cedrus
b) Pteris
c) Funaria
d) Polytrichum
17. T.O. Diener discovered a
a) free infectious DNA
b) infectious protein
c) bacteriophage
d) free infectious RNA
18. Montreal Protocol aims at?
a) biodiversity conservation
b) control of water pollution
c) control of carbon dioxide emission
d) reduction of ozone-depleting substances
19. Male and female gametophytes are independent and free-living in?
a) mustard
b) castor
c) Pinus
d) sphagnum
20. Which one of the following is not used in organic farming?
a) Glomus
b) Oscillatoria
c) Snail
d) Earthworm
Answers with Explanations
12. b) Thyroxine
13. c) Presence of vessel elements and absence of archegonia
14. c) Archaebacteria that lack any histones resembling those found in eukaryotes but
whose DNA is negatively supercoiled.
15. c) Salvinia
16. a) Cedrus
18. d) reduction of ozone-depleting substances
19. d) sphagnum
20.c) Snail